Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
Amodiaquine dihydrochloride dihydrate receptor The radiograp
2022-10-14
The radiographic correlate will be similarly important for the success of other non-VEGF TKIs, such as those targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor expressed in 50% of high-grade primary Amodiaquine dihydrochloride dihydrate receptor neoplasms. It has been reported that icotinib and gefitini
-
Angiogenesis refers to the formation of new
2022-10-14
Angiogenesis refers to the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature [1]. Physiological angiogenesis is necessary for key processes such as wound healing, tissue regeneration and repair. In pathological conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, and other pat
-
br Antiangiogenic therapy in non small
2022-10-14
Antiangiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Antiangiogenic targeted therapy is an area of active research in which numerous agents have been studied and have been shown to be effective for many tumor types including NSCLC. Angiogenesis is frequently upregulated in malignant solid
-
We also measured macrophage infiltration and CLS presence in
2022-10-14
We also measured macrophage infiltration and CLS presence in peri-gonadal AT from db/db mice and controls. CLS are morphological features within AT that are accurate indicators of adipocyte death and macrophage infiltration [56]. An earlier study showed that CLS macrophages account for >90% of the t
-
CCG 50014 While the mechanisms by which
2022-10-14
While the mechanisms by which ALDH2 regulates cardiac responses to pathological stress remain unclear, the capillary rarefaction found in pressure-overloaded ALDH2 Tg hearts provides potential clues. Loss of capillary density and diminished endothelial function occur in pathological hypertrophy [46]
-
br Introduction br Rac dependent ROS and actin regulation in
2022-10-14
Introduction Rac1-dependent ROS and Quinupristin-Dalfopristin Complex mesylate synthesis regulation in neuronal functions NOX-mediated ROS have an important role as physiological messengers. One remarkable example regarding such a function is during axonal formation. In this line, increased p4
-
Dorsomorphin The first suggestions that the cleaved intracel
2022-10-14
The first suggestions that the cleaved intracellular domain of APP, AICD, might transit to the nucleus and hence selectively regulate gene transcription arose from analogies with the Notch receptor signalling system where similar intra-membrane proteolysis occurs [84], [85] and it was later confirme
-
br LO and the secretase
2022-10-14
5LO and the γ-secretase complex Supporting this concept, during a recent trial testing the γ-secretase inhibitor semagacestat (LY 450139), AD patients actually experienced a functional decline compared to patients who took a placebo in addition to several other significant adverse effects (Doody
-
Most of lipid lowering agents have many
2022-10-13
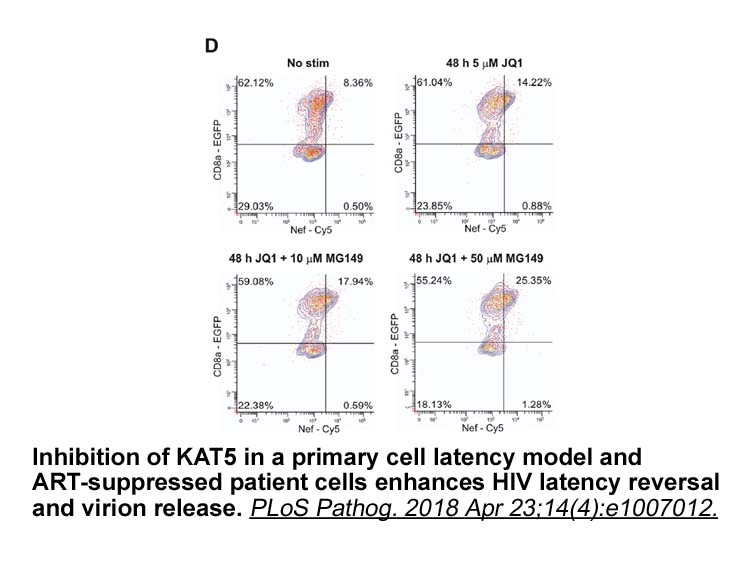
Most of lipid-lowering agents have many therapeutic problems with severe side effects, while dietary fibers as lipid lowering therapy are safer. Chitosan (CS) is a dietary fiber biodegradable, biocompatible and has many health benefits including wound healing, antiinflammatory, anti-cancers, immune-
-
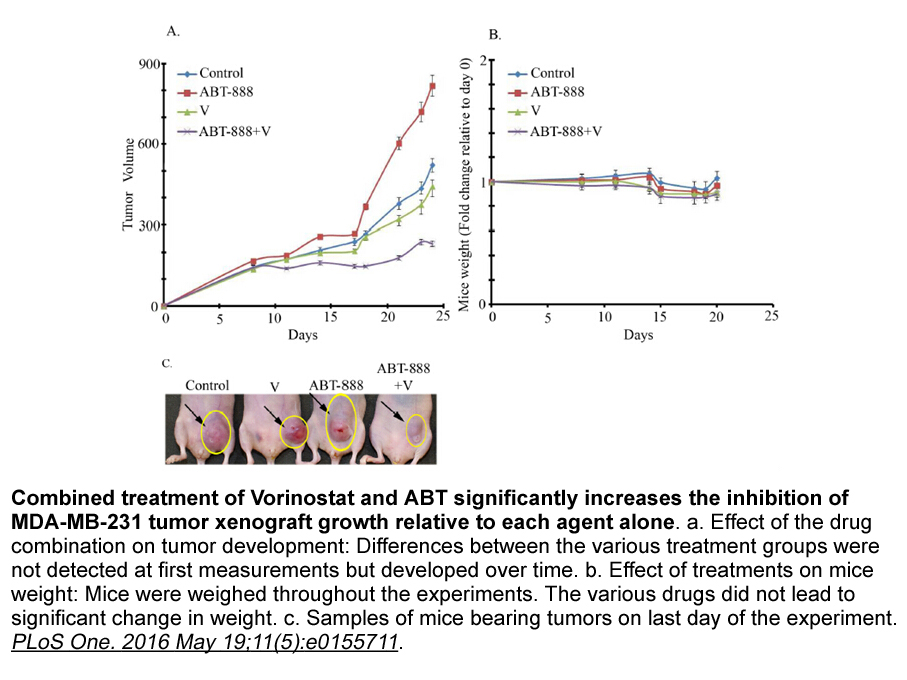
The Nagoya Heart Study enrolled patients with hypertension a
2022-10-13
The Nagoya Heart Study enrolled patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes or impaired Piperine tolerance (12). Patients were randomized to valsartan- or amlodipine-based regimens with a BP target of ≤130/80 mmHg. The primary outcome was a composite of sudden cardiac death, myocardial infarctio
-
Preclinical models indicate roles for adiponectin in the
2022-10-13
Preclinical models indicate roles for adiponectin in the maintenance of hepatic lipid metabolism. Adiponectin overexpression prevents accumulation of triglycerides or the deleterious lipid metabolites diacylglycerols or ceramides [5,8]. Direct manipulation of adiponectin expression demonstrates a po
-
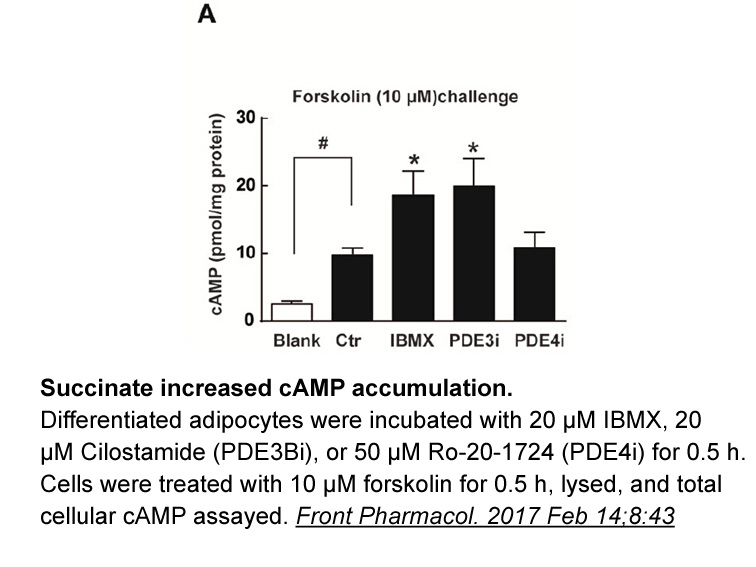
Pirarubicin Since forskolin is known to act directly at the
2022-10-13
Since forskolin is known to act directly at the catalytic site of adenylate cyclases near the ATP binding (Tesmer et al., 1997), the synergistic and/or permissive effect of gonadotropins on FSK activity must occur at the level of AC itself or very near, at the level of one of its direct partner. The
-
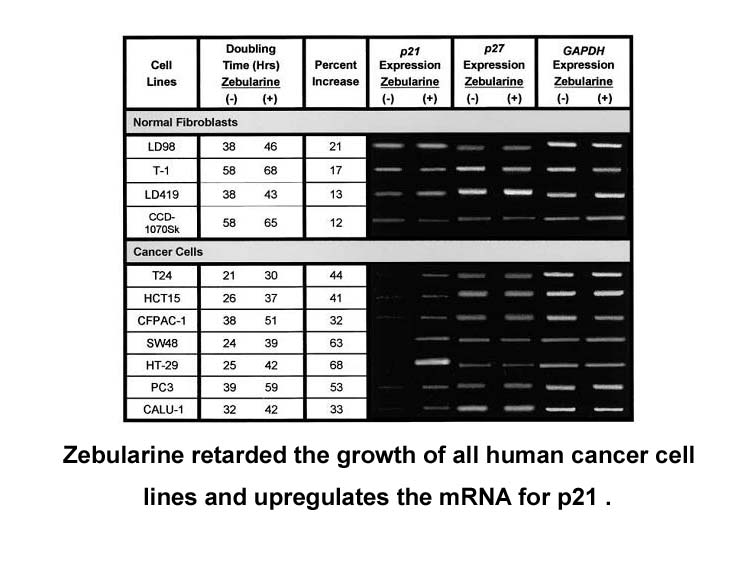
In conclusion re evaluation of HER status is necessary to
2022-10-12
In conclusion, re-evaluation of HER2 status is necessary to determine the appropriate use of anti-HER2–targeted therapy beyond disease progression. EGFR and c-met amplification, as well as PIK3CA mutation, are rarely associated with acquired resistance. Our results highlight the importance of formal
-
Several plant derived molecules such
2022-10-12
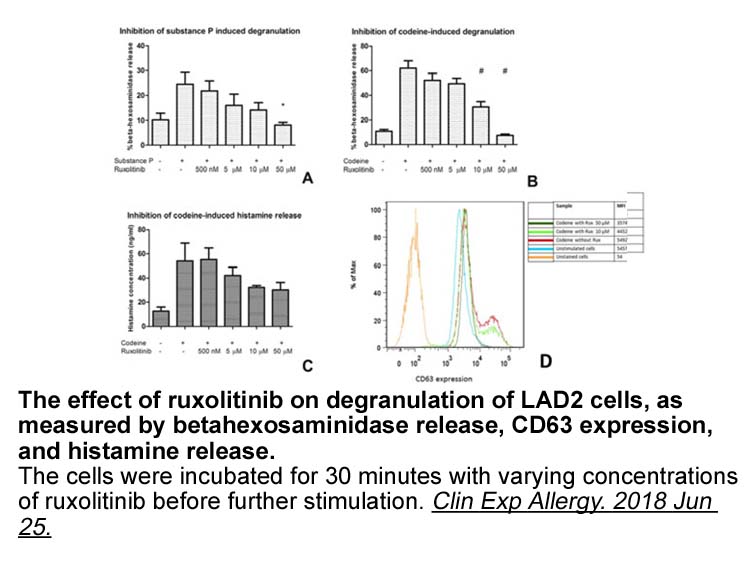
Several plant-derived molecules such as resveratrol, curcumin, zerumbone, and physalin B have been reported as modulators of Hh/Gli signaling pathway (Hosoya et al., 2008, Mohapatra et al., 2015). Our previous studies have demonstrated that a sesquiterpene lactone and diarylheptanoids from Siegesbec
-
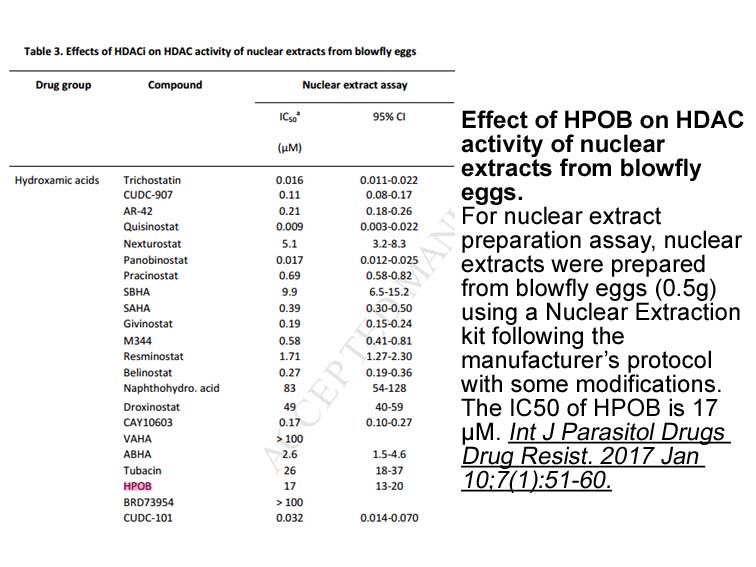
Epigenetic drugs such as HDAC
2022-10-12
Epigenetic drugs, such as HDAC inhibitors, regulate gene expression by affecting the activity of histone or DNA modifying enzymes and their associated transcriptional response [141]. BET bromodomain protein inhibition is another epigenetic approach for blocking the Hedgehog pathway at the downstream
11632 records 75/776 page Previous Next First page 上5页 7172737475 下5页 Last page